1、 Reduced contact area
When the surface flatness of IGBT chips is poor, the contact surface between the chip and the heat sink will no longer be completely adhered. Due to the unevenness of the chip surface, some areas will not be able to form effective contact with the heat sink, resulting in a decrease in contact area. The decrease in contact area means that the channel for heat transfer becomes narrower, and the efficiency of heat transfer will be affected.
2、 Increased contact thermal resistance
Contact thermal resistance is the resistance encountered when heat is transferred at the interface between two different materials. When the surface flatness of IGBT chips is poor, the contact between the chip and the heat sink will become less tight, resulting in gaps. The thermal conductivity of air in these gaps is much lower than that of metals, thus increasing the contact thermal resistance. The increase in contact thermal resistance can hinder heat transfer, making it difficult for the heat generated by the chip to be effectively transferred to the heat sink in a timely manner, thereby affecting the heat dissipation performance of IGBT.
3、 The impact on IGBT performance
Temperature rise: Due to the increase in contact thermal resistance, the heat generated by the chip cannot be dissipated in a timely manner, resulting in an increase in chip temperature. High temperature will accelerate the aging process of IGBT and shorten its service life.
Performance degradation: An increase in chip temperature can lead to a decrease in IGBT performance, such as slower switching speed and increased losses. These performance declines will directly affect the performance of IGBT in circuits.
Reduced reliability: Long term operation at high temperatures can decrease the reliability of IGBTs and increase the risk of their failure.
4、 Solution
Improving chip flatness: By improving the chip manufacturing process, the flatness of the chip surface can be increased to ensure a tight contact between the chip and the heat sink.
Optimize heat sink design: Adopt more efficient heat sink design, such as increasing heat dissipation area, optimizing heat dissipation structure, etc., to improve heat dissipation efficiency.
Use thermal conductive medium: Apply thermal conductive medium (such as thermal conductive silicone grease) between the chip and the heat sink to fill the gap and reduce contact thermal resistance. The selection of thermal conductive medium should ensure good and stable thermal conductivity.
In summary, poor surface flatness of IGBT chips can have adverse effects on the contact area and thermal resistance between the chip and the heat sink, thereby affecting the performance and reliability of IGBT. Therefore, in the manufacturing and packaging process of IGBT, it is necessary to strictly control the flatness of the chip surface and take effective heat dissipation measures to ensure the stable operation of IGBT.
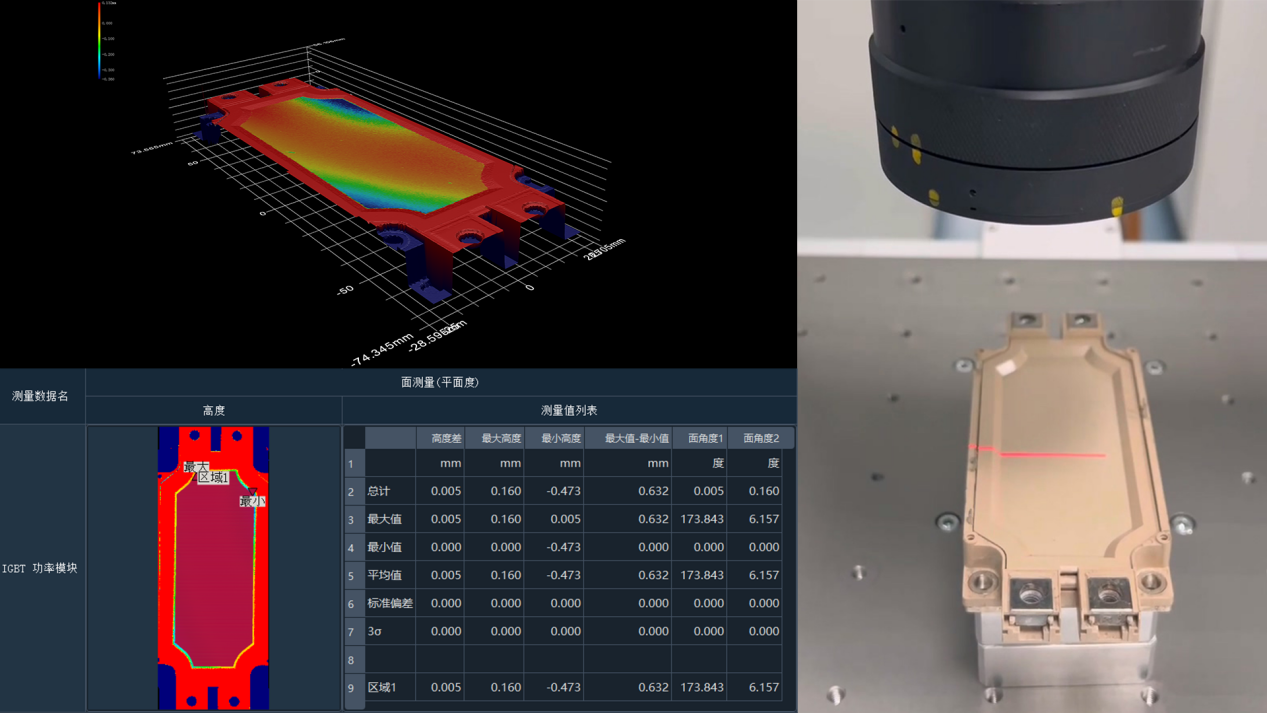
IGBT package bonding flatness test case: (Color temperature chart represents 3D high and low information, table shows measured deformation)
4、 Introduction to Laser Frequency Comb 3D Optical Contour Measurement System
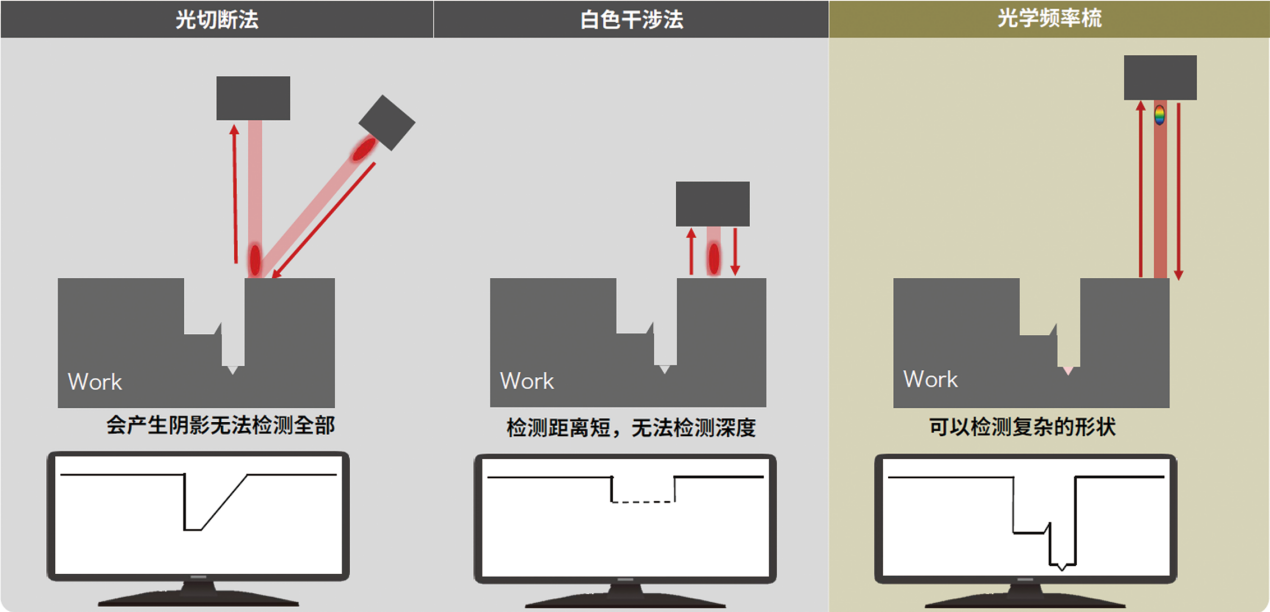
The laser optical frequency comb 3D contour measurement system utilizes the principle of laser frequency comb and adopts high-frequency laser pulse flight distance measurement method, which is not afraid of traditional optical obstruction problems and fully applicable to the measurement of various complex large structural components, solving the difficulties of traditional optical measurement such as deep holes and grooves. The laser frequency of 500kHz has brought technological innovation to the automation of detection.
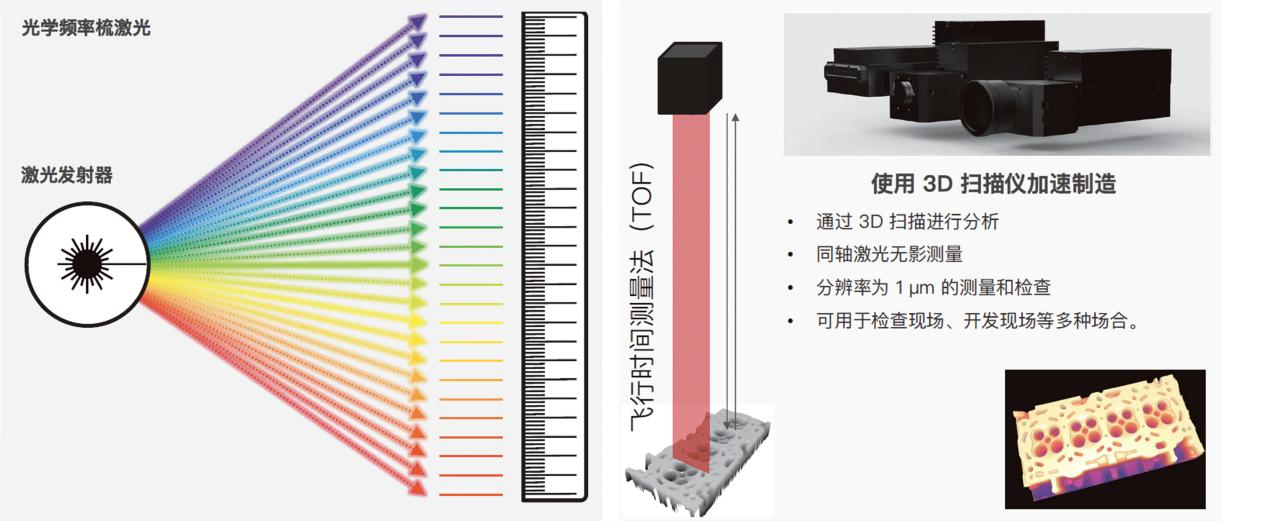
Technical feature one: coaxial shooting, flight ranging scanning method, not afraid of traditional optical "obstruction" problems.
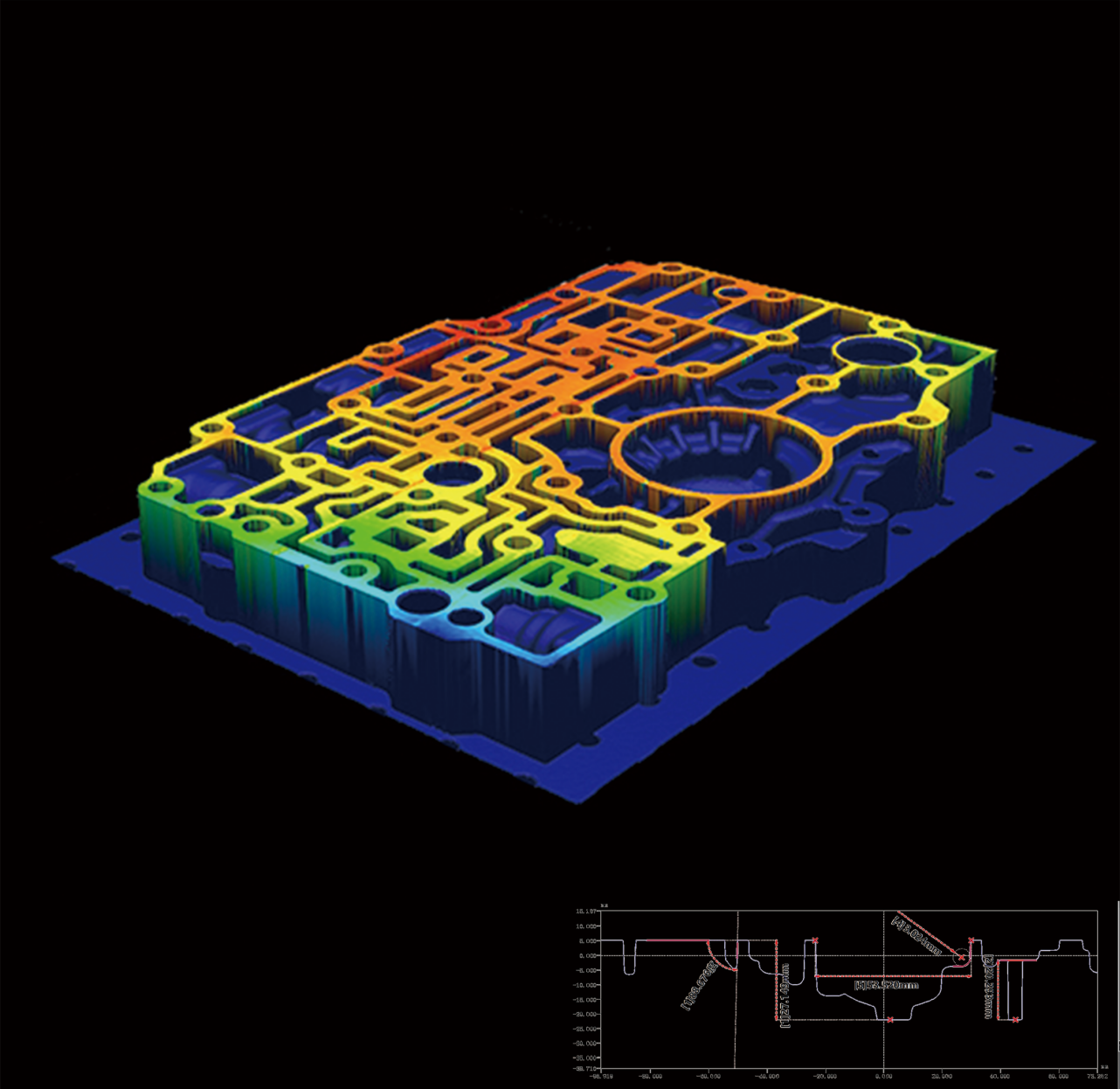
Actual case: Valve body oil circuit board with vertical and horizontal grooves
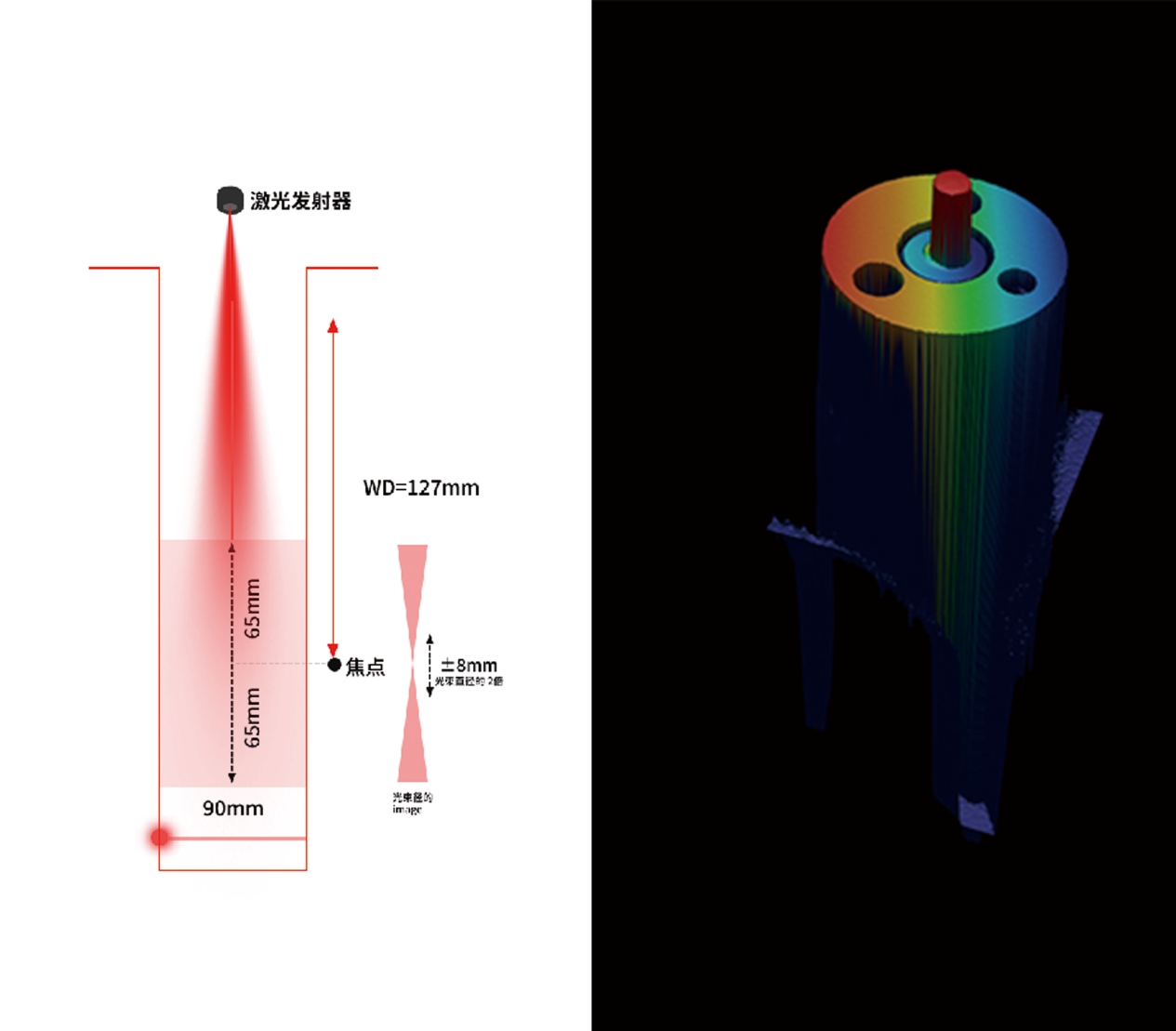
Technical feature 2: With an accuracy of ± 2um, it can achieve a maximum height/depth scanning imaging of 130mm
Technical feature three: It can be equipped with multiple lens combinations to achieve scanning with a large field of view of tens of meters.