The interference effect used in modern white light interferometers occurs when the reflected light from the sample overlaps with the light reflected from the high-precision reference mirror.
The measurement method is based on the Michelson interference principle, and its optical configuration (image) includes a light source with a coherence length in the range of μ m. The collimated beam is split into a measurement beam and a reference beam on the beam splitter. Measure the sample illuminated by a beam of light, and reference the beam to a mirror. The light reflected from the mirror and sample is recombined at the beam splitter and focused onto the camera.
Whenever the optical path of the object point in the measuring arm is the same as that in the reference arm, all wavelengths in the light source spectrum undergo constructive interference, and the intensity of the camera pixel of the object point in question is the highest. For objects with different light paths, the intensity of the assigned camera pixels is lower. Therefore, the camera records all image points at the same height.
Instruments with telecentric configuration allow you to measure the shape of large surfaces simultaneously and quickly at once. If high lateral resolution is required, the microscope system is more suitable when the optical configuration, including the reference arm, is integrated into the lens.
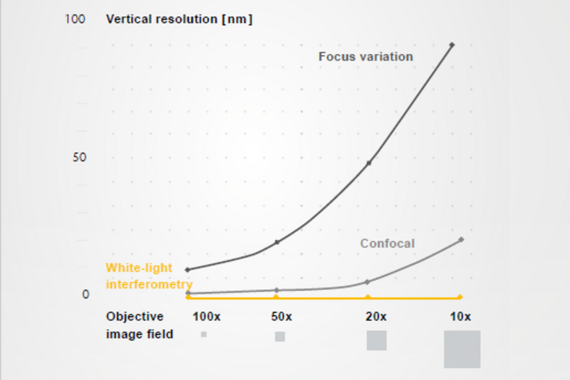
Using white light interferometry, high vertical resolution is independent of the field of view
Vertical resolution is independent of the field of view
When using white light interferometry (coherent scanning interferometry) for planar measurement, the vertical resolution does not depend on the selected objective lens. White light interferometry is the only measurement method whose resolution is independent of the field of view.